Forget the NFT trading bust—Non-fungible tokens will rule our world
NFTs as 'utility' tokens are booming. Gamers, social networks, entertainers, and top high-end brands leverage NFTs to attract, authenticate, manage, and serve next-generation customers.

The NFT boom and bust
Before we get more specific on how NFTs will take over the world, let’s zoom up for a moment and address the dinosaur in the room: WTF was up with that crazed NFT hysteria in late 2021? Are these NFTs for real?
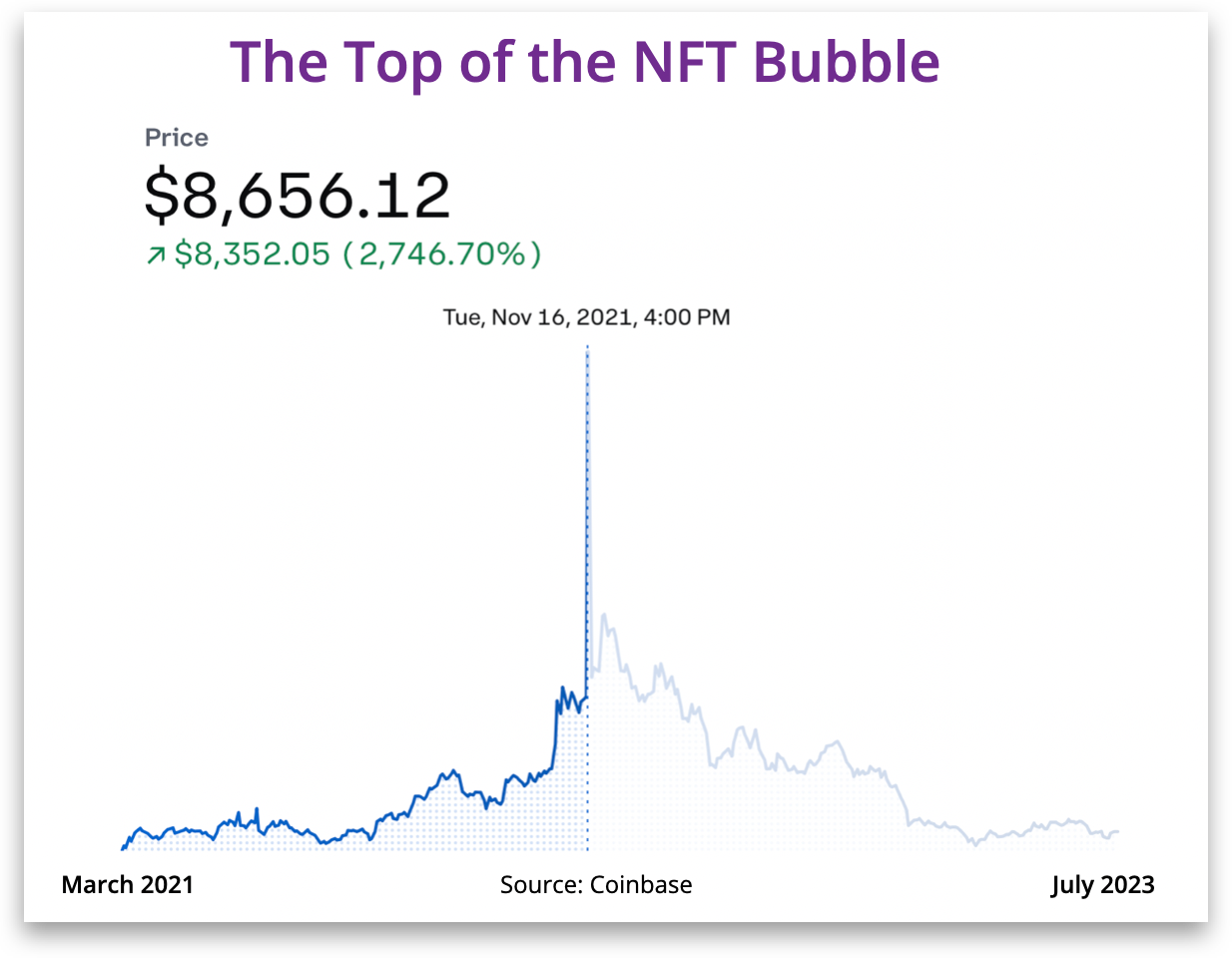
The answer to the first question is illustrated above. A subset of largely Zoomers started maniacally trading NFTs and drove an insane three-month price run-up starting in August of 2021, only to see values take a dramatic swan dive three months later. When the dust cleared, the NFT craze won the prize as the greatest collective investor blip of all time. It was clear to the sane from the beginning that the value proposition (or lack thereof) driving the 2021 NFT trading craze would never meet the fantasies of early enthusiasts. NFT trading is still with us but with a more traditional and (hopefully) reasoned collectibles investor-valuation sensibility. But this world is just a sideshow to the booming applications of NFTs across the largest industries in the world.
Epic NFT rug-pulling
Iranian-born crypto entrepreneur Sina Estavi bought the NFT representing Twitter founder Jack Dorsey’s first-ever tweet in March 2021 for $2.9 million.
A year later, Mr. Estavi ambitiously listed the NFT for sale again at $48 million. Prior to the listing, he admirably pledged to share half of his profits (presumably $25 million) to charity. Such a noble cause! The problem was that when the auction was over, the highest bid came in a $277.
Publicly trading NFTs only represent a small subset of the overall NFT market. Most NFTs fall under the category of ‘utilities.’ For example, gaming companies use NFTs to validate member identity, permit community privileges, and offer in-game items as collectibles. Since gaming transactions represented over half of all blockchain activity in 2022, the most popular use of NFTs today is in the gaming industry; this trend bodes well for overall NFT proliferation. “I am an NFT maximalist. In 18–24 months from now, I think we’re just going to see this onslaught of (NFT-based) games, and that’s something that everybody can understand and participate in,’ says Avichal Garg, CEO and co-founder of the $1.6 billion VC fund Electric Capital.
Gaming Companies with NFTs
Gods Unchained (GODS) — A collectible card game where players can buy, sell, and trade rare cards as NFTs.
CryptoKitties — A game where players can collect, breed, and trade digital cats as NFTs.
F1 Delta Time — A racing game where players can buy and trade unique cars and other in-game assets as NFTs.
Aavegotchi (GHST) — A game that combines NFTs and DeFi, where players can collect, train, and battle ghost-like creatures called Aavegotchis.
Splinterlands — A collectible card game where players can buy, sell, and trade cards as NFTs and battle other players for rewards.
Gala Games — A platform that hosts games using NFTs for in-game items and assets, including Townstar, Mirandus, and Fortified.

Another example is the social network Reddit that now offers members limited-edition NFT profile avatars created by independent artists. Instagram creators will soon sell their digital collectible NFTs to fans on and off Instagram. Reddit now offers members limited-edition NFT profile avatars created by independent artists. Youtube also allows creators to sell content as NFTs so fans can ‘own’ videos.
Further, NFTs are mashing with high-end consumer brands, entertainers, and influencers to market and monetize unique content and connection. For example, soccer sensation Cristiano Ronaldo dropped an NFT collection to drive fan engagement and access other future perks. French fashion house Dior is the latest luxury brand to embrace blockchain, announcing a limited-run B33 sneaker for men with an NFT-based certificate of ownership for the available 470 pairs at $1,350.

NFTs for high-end consumer goods
Click each brand name to see their NFT marketing tactics in action:
Adidas, Lamborghini, Tiffany & Co, Disney, Louis Vuitton, Nike, Porsche, NBA, Burberry, Netflix, Tag Heuer, Visa, Timex, Prada, BMW, NFL, Gucci, Ray-Ban, Cartier, Red Bull, Lacoste, Australian Open, Heineken, Marc Jacobs, Audi, Hugo Boss, Mastercard, Hermes, McLaren, and Ralph Lauren.
So the answer to the second question is also a bellowing Yes! The long-term utility value of NFTs to enhance the experience of hospitality, gaming, entertainment, and social networks and transform consumer marketing and customer loyalty represents a gigantic economic opportunity. Trading NFT collectibles will also be a sideshow to a much bigger event.
What is a non-fungible token (NFT)?
An NFT is a unique digital identifier recorded on a public blockchain as a certificate of authenticity and proof of ownership of a variety of digital files, such as artwork, photos, videos, audio, and in-game virtual goods. The NFT format also makes it easy for the owner to transfer, trade, and sell their assets. NFTs cannot be copied, substituted, or subdivided. Because NFTs are uniquely identifiable, they differ from cryptocurrencies, such as Bitcoin, which are fungible. Anybody can create NFTs as it requires few or no coding skills. NFTs first kicked off in the art and collectible business as digital trading cards.
Zooming way up, our definition of Web3 sees the blockchain and digital assets (cryptos + NFTs) as the new decentralized internet paradigm, with AI as the ‘smart engine’ and the metaverse as an emerging and powerful new way to visualize and engage with data and connect with each other. From the global Silicon Valley perspective, this represents a $100 trillion opportunity.
Our bet is different creative variations of NFT will serve as an immutable certificate of ownership for a vast array of asset categories, including vehicles, boats, real estate deeds, patents, precious metals, event tickets, and coins. The NFT format makes assets more portable, tradable, and liquid. NFTs also smooth out the transfer of ownership process between parties and lower the risks of fraudulent or stolen goods.

Already the California DMV is moving towards offering an NFT-based vehicle ownership certificate (a.k.a. “pink slip”). "Blockchain will allow for a vehicle title to be a secure digital asset (NFT) that can be held in a DMV digital wallet, eliminates the need for a paper title, and indisputably validates who owns the asset,” says DMV chief digital officer Ajay Gupta.
In addition, our future birth and graduate certificates, driver’s licenses, citizenship and social security cards, academic transcripts, professional certifications, PDFs, tax returns, credit reports, and medical records will be granted to us in blockchain-based NFT form. We will hold our NFTs in our digital wallets and maintain some offline distributed storage networks that are impossible to hack. Every digital document will live on the blockchain within the next ten years.
NFTs will be a big part of our future, as we have barely tapped the potential. Whether on a personal level or business.
Understanding Blockchain
A blockchain was created by a person (or group of people) under the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto in 2008 to serve as the publicly distributed ledger for Bitcoin cryptocurrency transactions, based on previous work by Stuart Haber, W. Scott Stornetta, and Dave Bayer. Implementing the blockchain within Bitcoin made it the first digital currency to solve the double-spending problem without needing a trusted authority or central server. The Bitcoin design has inspired other applications and blockchains that are readable by the public and are widely used by cryptocurrencies. The blockchain may be considered a type of payment rail.
A blockchain is a distributed ledger with growing lists of records (blocks) securely linked together via cryptographic hashes. Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, a timestamp, and transaction data. The timestamp proves that the transaction data existed when the block was created. Since each block contains information about the previous block, they effectively form a chain (compare linked list data structure), with each additional block linking to the ones before. Consequently, blockchain transactions are irreversible because, once they are recorded, the data in any given block cannot be altered retroactively without altering all subsequent blocks.
Blockchains are typically driven by smart contract technology that allows self-executing programs to automate transactions based on pre-set conditions. These apps are managed by a peer-to-peer (P2P) computer network for use as a public distributed ledger, where nodes collectively adhere to a consensus algorithm protocol to add and validate new transaction blocks. Although blockchain records are not unalterable, blockchains may be considered secure by design and exemplify a distributed computing system with high Byzantine fault tolerance since blockchain forks are possible.
The bottom line is smart contract-driven decentralized blockchain applications empower users with what we all want: autonomy, security, and privacy. Web3 aims to fulfill the original vision for the web. In this decentralized, trustless, permissionless world, we control our data and interact peer-to-peer and peer-to-merchant without the need for centralized powers who control our data and online activities.